Redefining the Radio Access Network (RAN) with 5G Open RAN (ORAN)
By Shirish Nagaraj
Published: October 12, 2022
Our wireless industry has been at the forefront of change with the advent of data and video transforming the way we communicate and connect with each other. While the underlying wireless infrastructure has evolved tremendously over the years, the vendor ecosystem has been limited to a few companies leading to a closed architecture which has perhaps curtailed growth.
The wireless industry could be on the precipice of a revolution in which all this may change. The wireless infrastructure of the future may rely increasingly on flexible, scalable, open architecture and we are pleased to share that Corning is spearheading the development of the game-changing Open Radio Access Network (ORAN) that is redefining the RAN ecosystem for 5G. While ORAN could be the way of the future, a balanced RAN approach will prevail in the coming few years where the proven centralized RAN (CRAN) and the new ORAN will co-exist. Increasingly 5G will leverage an ORAN architecture, with the expectation that 6G and beyond will be based primarily on an ORAN architecture leading to vendor diversity and higher performance.
Corning has extensive experience with in-building wireless networks, and we have now taken a leading position in the work being conducted in our industry around ORAN delivering 5G indoors. Over the coming weeks, we will share with you our insight about where ORAN is today and where we believe it is heading. We will be detailing how 5G ORAN will be imperative for the future of in-building wireless infrastructure and the key considerations for building open networks of the future.
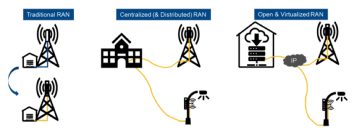
ORAN 101 – Understanding Open Radio Access Network (ORAN)
Over the decades, RANs have been vendor and carrier centric operating in a closed environment. In the past few years, the CRAN architecture affected a major topology change with baseband units (BBUs) aggregated in CRAN hubs and dedicated fiber runs to cell sites. Reduced latency, higher performance, and reduced infrastructure costs were realized in CRAN deployments.
However, CRANs are also limited by their closed architecture with vendor lock-in erecting barriers to entry for best-in-class component providers. The introduction of ORAN could change everything, and we have a lot to look forward to in the industry with 5G ORAN poised to deliver huge benefits for the mobile network operators (MNOs) and building owners (REITs).