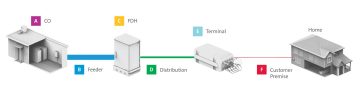
Rural communities have a historic opportunity to lay the foundation for a broadband infrastructure that can deliver high-quality broadband to everyone for generations to come. Building the right broadband networks now will have a long-reaching impact on your community. As communities build out broadband infrastructure, choosing the right architecture is key to ensuring seamless connectivity. There are three primary broadband architecture types to consider: distributed split, centralized split, and optical tap.
A distributed split architecture involves spreading out the network equipment across various locations, which helps reduce the physical volume of products in the field. It is known for its flexibility and scalability, making it a popular choice for expanding networks in rural areas.
A centralized split architecture is where most of the network equipment is in a central hub, which then distributes the signal to different locations. It is known for its simplicity and ease of maintenance.
An optical tap architecture uses a unique approach through the use of a single fiber. It is designed to split and distribute the signal at the same time, reducing the amount of fiber required. It is an efficient system that minimizes signal loss leading to better performance.
As you make decisions about your community’s network, there are a range of fiber network architecture options from which to choose. Leverage the resources below to make the best decision possible.